what is webpage, websites, webserver.......
How the Web Works?
Before entering into this topic the terms which we can heard most commonly is
Webpage - A webpage is a specific collection of information provided by website and displayed to a user in a web browser.
Websites - A website is a collection of webpages and related content that is identified by a common domain name and published on at least one web server.
Examples : Wikipedia.org , google.com , amazon.com
Web browser - A web browser is a software application for accessing information on the World Wide Web. When the user request a web page from a particular site, the web browser retrieves the necessary content from the web server and displays the page on the user's device.
Web server - A webserver is a server software, or a system of one or more computers dedicated to running this software, that can satisfy client HTTP requests on the public World Wide Web or also on private LANs and WANs.
When you visit a website, the web server hosting that site could be anywhere in the world. In order for you to find the location of the web server, your browser will first connect to a Domain Name System (DNS) server.
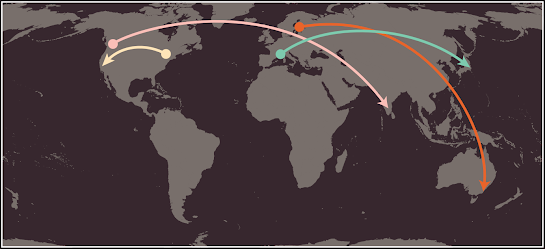
Below image you can see examples that demonstrate how the web server that hosts the website you are visiting can be anywhere in the world. It is the DNS servers that tell your browser how to find the website.
- A user in Barcelona visits sony.jp in Tokyo
- A user in New York visits google.com in San Francisco
- A user in Stockholm visits qantas.com.au in Sydney
- A user in Vancouver visits airindia.in in Bangalore
Process 1:
- When you connect to the web, you do so via an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- You type a domain name or web address into your browser to visit a site; for example: google.com, bbc.co.uk, microsoft.com
Process 2:
- Your computer contacts a network of servers called Domain Name System (DNS) servers.
- These act like phone books; they tell your computer the IP address associated with the requested domain name.
- An IP address is a number of up to 12 digits separated by periods / full stops.
- Every device connected to the web has a unique IP address; it is like the phone number for that computer.
Process 3:
- The unique number that the DNS server returns to your computer allows your browser to contact the web server that hosts the website you requested.
- A web server is a computer that is constantly connected to the web, and is set up especially to send web pages to users.
Process 4:
- The web server then sends the page you requested back to your web browser.



Yes you are right.
ReplyDelete